ml4eft.analyse.analyse.Analyse
ml4eft.analyse.analyse.Analyse#
- class ml4eft.analyse.analyse.Analyse(path_to_models, order='quad', all=False)[source]#
Bases:
objectPost-training analyser that loads and evaluates models
- __init__(path_to_models, order='quad', all=False)[source]#
Analyse constructor
- Parameters
path_to_models (dict) – Of the form {‘lin’: {‘c1’:
<path_to_c1_models>, ‘c2’:<path_to_c2_models>}, ‘quad’: {‘c1_c1’:<path_to_c1_c1_models>}, {‘c1_c2’:<path_to_c1_c2_models>}, {‘c2_c2’:<path_to_c2_c2_models>}}order (str, default='quad') – The order in the EFT expansion (choose between either ‘lin’ or ‘quad’)
all (bool, default='True') – When set to True, the analyser loads all replicas. Set to False by defualt, in which case the replicas are clusterd into “good” and “bad” models based on their loss value.
Examples
Trained models can be loaded by creating an
ml4eft.analyse.analyse.Analyseobject>>> analyser = Analyse(path_to_models, 'quad')
Followed by constructing a model dictionary that contains all the models plus associated settings
>>> analyser.build_model_dict() >>> analyser.model_df models idx scalers run_card rep_paths lin c1 [Classifier() ... [rep_idx, ...] [RobustScaler(quantile_range=(5,95)), ...] {'name': 'c1', ...} [<path_to_rep>, ...] c2 [Classifier() ... ... ... ... ... quad c1_c1 [Classifier() ... ... ... ... ... c1_c2 [Classifier() ... ... ... ... ... c2_c2 [Classifier() ... ... ... ... ...
Events and the inclusive cross-section can be loaded into a DataFrame by
>>> df, xsec = analyser.load_events('.../events_<rep>.pkl.gz') >>> df sqrts_hat pt_l1 pt_l2 pt_l_leading pt_l_trailing ... 1 1702.356400 20.532279 308.295118 308.295118 20.532279 ... 2 ... ... ... ... ...
To evaluate the models on the loaded DataFrame
df, use:>>> analyser.evaluate_models(df) >>> analyser.models_evaluated_df['models'] >>> analyser.models_evaluated_df['models'] lin c1 [[0.05130317, 0.05723376, 0.058220766, 0.04042... c2 [[0.074420996, 0.10293982, 0.10705493, 0.05695... quad c1_c1 [[0.07958487, 0.13463444, 0.14215767, 0.049889... c1_c2 [[0.0005354581, 0.00042073405, 0.0004430262, -... c2_c2 [[0.00032746396, 0.00041523552, 0.00045115477,...
Methods
__init__(path_to_models[, order, all])Analyse constructor
accuracy_heatmap(c_name, order, process[, ...])Compares the NN and true EFT ratio functions and plots their ratio and pull
build_model_dict([rep, epoch])Constructs a DataFrame with loaded models plus associated info
build_path_dict(root, order, prefix)Construct path to model dictionary
coeff_function_truth(df, c_name, features, ...)Evaluates the analytic EFT ratio functions \(r_{\sigma}^{(i)}\) and \(r_{\sigma}^{(i,j)}\)
decision_function_nn(c[, df, epoch])Computes the Neural Network parameterised decision function \(g(x, c)\)
decision_function_truth(events, c, features, ...)Computes the analytic decision function
evaluate_models(df[, rep, epoch])Evaluates the loaded models on a Pandas DataFrame
dffilter_out_models(losses)Filter out the badly trained models based on kmeans clustering.
get_event_paths(root_path)Returns a list of paths to the DataFrames at
root_pathlikelihood_ratio_nn(c[, df, epoch])Compute the Neural Network parameterised likelihood ratio
likelihood_ratio_truth(events, c, features, ...)Computes the analytic likelihood ratio \(r(x, c)\)
load_events(event_path)Loads a event DataFrame and splits it into the events and the inclusive cross section
load_loss(path_to_loss)Loades the losses per epoch into a list
load_models(model_path[, rep, epoch])Loads the trained models
load_run_card(path)Loads training run card
plot_accuracy_1d(c, c_name, process, order, ...)Plots the decision boundary \(g(x,c)\) as predicted by the ML model and the analytical (exact) model along 1 dimension, i.e :x=math:m_{tt}
plot_heatmap(ax, data, xlabel, ylabel, ...)Plot and return a heatmap of
dataplot_heatmap_overview(c_name, order, process)Produces an overview of heatmaps showing in each plot the ratio between the ML model prediction and the analytical EFT ratio function \(r_{\sigma}^{(i)}\) or \(r_{\sigma}^{(i, j)}\)
plot_loss_overview(c_name, order[, ax, rep, ...])Plots the loss evolution per replica and returns an overview plot
point_by_point_comp(df, c_name, c, features, ...)Produces a point by point comparison overview per replica of the log-likelihood ratio between the ML model and the analytical (exact) model
point_by_point_comp_med(df, c, features, ...)Produces a point by point comparison of the log-likelihood ratio between the (median) ML model and the analytical (exact) model
posterior_loader(path)Loads the posterior samples at
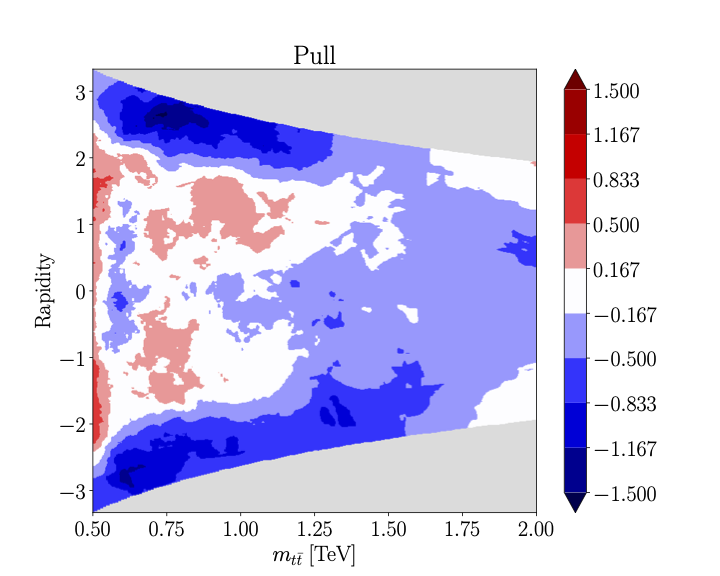
pathand converts it to a DataFrame- accuracy_heatmap(c_name, order, process, mx_cut=None, rep=None, epoch=- 1, ax=None, text=None)[source]#
Compares the NN and true EFT ratio functions and plots their ratio and pull
- Parameters
c_name (str) – Name of the EFT parameter, e.g. ‘ctgre’
order (str) – Order in the EFT expansion, options are ‘lin’ or ‘quad’
process (str) – Specifies the process. Currently supported is ‘tt’ and ‘ZH’
mx_cut (list, optional) – Plot range of the invariant mass
rep (int, optional) – Request to plot for a specific replica
epoch (int, optional) – Request to plot for a specific epoch.
ax (matplotlib.pyplot.axes, optional) – Axes to plot on
text (str, optional) – Add additional text on the heatmap such as the replica number
- Returns
matplotlib.figure.Figure – Heatmap of EFT ratio function
matplotlib.figure.Figure – Heatmap of associated pull
Examples
For a single EFT coefficient \(c_{tG}\) the likelihood ratio takes the form
\[r_{\sigma}(x, c_{tG}) = 1 + c_{tG} r_{\sigma}^{(c_{tG})} + c_{tG}^2 r_{\sigma}^{(c_{tG}, c_{tG})}\]To plot for example the accuracy of \(r_{\sigma}^{(c_{tG}, c_{tG})}\) by plotting its ratio to the exact result, one runs
>>> fig_med, fig_pull = analyser.accuracy_heatmap('ctgre_ctgre', 'quad', 'tt') >>> fig_med
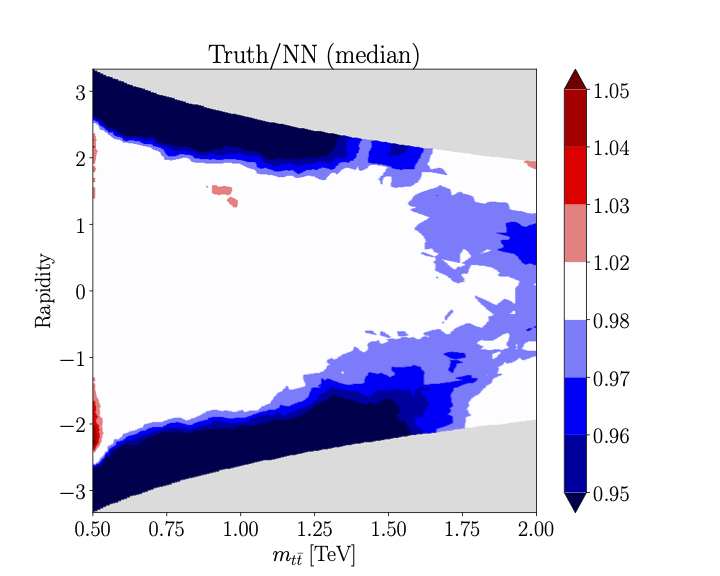
>>> fig_pull
- build_model_dict(rep=None, epoch=- 1)[source]#
Constructs a DataFrame with loaded models plus associated info
- static build_path_dict(root, order, prefix)[source]#
Construct path to model dictionary
- Parameters
- Returns
path_to_models – Dictionary containing the paths to the models for each EFT ratio function
- Return type
- coeff_function_truth(df, c_name, features, process, order)[source]#
Evaluates the analytic EFT ratio functions \(r_{\sigma}^{(i)}\) and \(r_{\sigma}^{(i,j)}\)
- Parameters
df (pandas.DataFrame) – Events on which to evaluate \(r_{\sigma}^{(i)}\) and \(r_{\sigma}^{(i,j)}\)
c_name (str) – Name of the EFT coefficient. Choose between ‘ctgre’, ‘cut’, ‘cut_cut’, ‘ctgre_ctgre’
features (list) – Kinematic features, options are
m_tt,yprocess (str) – Supported options are ‘tt’ or ‘ZH’
order (str) – Order of the EFT expansion, choose between ‘lin’ and ‘quad’
- Returns
coeff –
(N,) ndarraywith \(r_{\sigma}^{(i)}\) or \(r_{\sigma}^{(i,j)}\) evaluated ondfdepending on theorder- Return type
array_like
- decision_function_nn(c, df=None, epoch=- 1)[source]#
Computes the Neural Network parameterised decision function \(g(x, c)\)
- Parameters
- Returns
decision_function – NN decision function
- Return type
- decision_function_truth(events, c, features, process, order=None)[source]#
Computes the analytic decision function
- Parameters
order (str, optional) – Specifies the order in the EFT expansion. Must be one of
lin,quad.process (str) – Choose between
ttorZHfeatures (list) – List of kinematic labels
events (pd.DataFrame) – Pandas DataFrame with the events
c (numpy.ndarray, shape=(M,)) – EFT point in M dimensions, e.g c = (cHW, cHq3)
- Returns
decision_function – Truth decision function
- Return type
- evaluate_models(df, rep=None, epoch=- 1)[source]#
Evaluates the loaded models on a Pandas DataFrame
df
- filter_out_models(losses)[source]#
Filter out the badly trained models based on kmeans clustering.
- Parameters
losses (array_like) – Losses of all the trained models
- Returns
good_model_idx – Array indices of the ‘good’ models
- Return type
- static get_event_paths(root_path)[source]#
Returns a list of paths to the DataFrames at
root_path- Parameters
root_path (str) – path to the DataFrame directory
- Returns
event_paths – list of paths to the DataFrames at stored at
root_path- Return type
Examples
The paths to the event DataFrames stored at
root_pathcan be loaded for ‘n_rep’ replicas by>>> analyser.get_event_paths('/training_data/tt_llvlvlbb/tt_c1') [/training_data/tt_llvlvlbb/tt_c1/events_0.pkl.gz', ... , /training_data/tt_llvlvlbb/tt_c1/events_<n_rep>.pkl.gz']
- likelihood_ratio_nn(c, df=None, epoch=- 1)[source]#
Compute the Neural Network parameterised likelihood ratio
- Parameters
c (dict) – Of the form {‘c1’: value, ‘c2’: value, …}
df (pandas.DataFrame, optional) – In case the loaded models have not been evaluated yet, one can pass
dfto evaluate the neural networksepoch (int, optional) – Specify an epoch if necessary, takes the best model by default
- Returns
ratio – likelihood ratio as
(N,M) ndarraywithNandMthe number of replicas and events respectively- Return type
array_like
- static likelihood_ratio_truth(events, c, features, process, order=None)[source]#
Computes the analytic likelihood ratio \(r(x, c)\)
- Parameters
- Returns
ratio – Likelihood ratio wrt the SM
- Return type
- static load_events(event_path)[source]#
Loads a event DataFrame and splits it into the events and the inclusive cross section
- Parameters
event_path (str) – Path to the DataFrame (including the xsec as first row)
- Returns
events (pandas.DataFrame) – DataFrame with events
xsec (float) – Inclusive cross-section of the events
- load_models(model_path, rep=None, epoch=- 1)[source]#
Loads the trained models
- Parameters
- Returns
models (array_like) –
(N,) ndarraycontaining the loaded neural networksmodels_rep_nr (array_like) –
(N,) ndarraycontaining the replica numbers of the loaded neural networksscalers (array_like) –
(N,) ndarraycontaining the preprocessing scalers of the loaded neural networksrun_card (dict) – training run card of the trained models
rep_paths (array_like) –
(N,) ndarraywith the paths to the neural networks
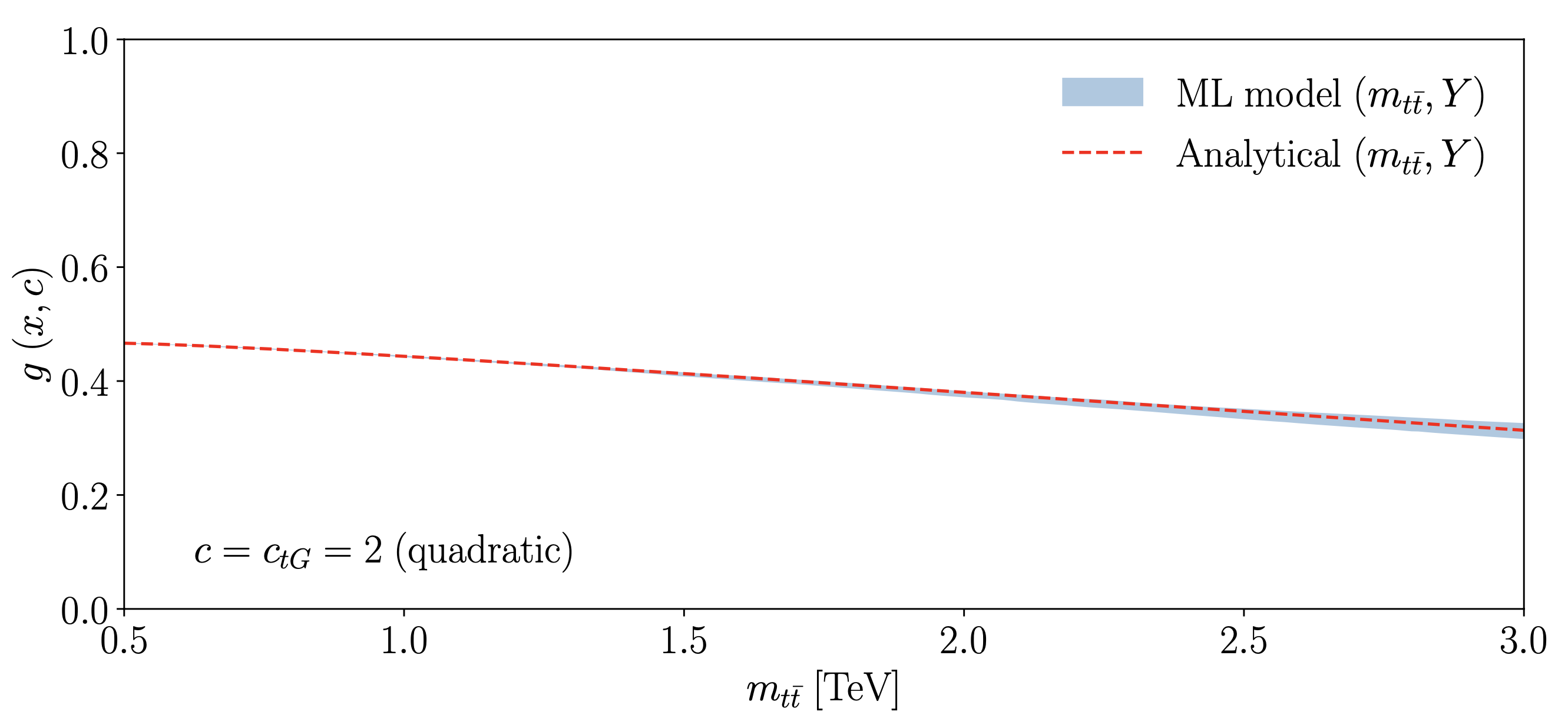
- plot_accuracy_1d(c, c_name, process, order, mx_cut, epoch=- 1, ax=None, text=None)[source]#
Plots the decision boundary \(g(x,c)\) as predicted by the ML model and the analytical (exact) model along 1 dimension, i.e :x=math:m_{tt}
- Parameters
c (dict) – Of the form {‘c1’: value, ‘c2’: value}
process (str) – Choose between
ttorZHorder (str, optional) – Specifies the order in the EFT expansion. Must be one of
lin,quad.mx_cut (list) – Plot range of the invariant mass
epoch (int, optional) – Specific epoch to plot, set to the best models by default
ax (matplotlib.axes, optional) – Plot on an already created axes object
text (str, optional) – Additional text to show on the plot
- Returns
fig – Plot comparing the decision boundary \(g(x,c)\) as predicted by the ML model and the analytical (exact) result
- Return type
matplotlib.figure
Examples
>>> analyser = Analyse(path_to_models, 'quad') >>> fig = analyser.plot_accuracy_1d(c={'ctgre': -2, 'cut': 0}, process='tt', order='quad', cut=0.5, text=r'$c=c_{tG}=2\;\mathrm{quadratic}$') >>> fig
- static plot_heatmap(ax, data, xlabel, ylabel, title, extent, bounds, cmap='GnBu', rep=None, text=None)[source]#
Plot and return a heatmap of
data- Parameters
data (numpy.ndarray, shape=(M, N)) – Input array
xlabel (str) – x-label
ylabel (str) – y-label
title (str) – title of plot
extent (list) – boundaries of the heatmap, e.g. [x_0, x_1, y_1, y_2]
bounds (list) – The boundaries of the discrete colourmap
cmap (str) – colourmap to use, set to ‘GnBu’ by default
- Returns
fig
- Return type
matplotlib.figure.Figure
- plot_heatmap_overview(c_name, order, process, mx_cut=None, reps=None, epoch=- 1)[source]#
Produces an overview of heatmaps showing in each plot the ratio between the ML model prediction and the analytical EFT ratio function \(r_{\sigma}^{(i)}\) or \(r_{\sigma}^{(i, j)}\)
- Parameters
c_name (str) – Name of EFT coefficient
order (str) – Order in the EFT expansion
process (str) – Specifies the process, choose between ‘tt’ and ‘ZH’
mx_cut (float, optional) – Plot range of the invariant mass
reps (int, optional) – Number of replicas to include in the heatmap overview
epoch (int, optional) – Specific epoch to plot at, takes the best models by default
- Returns
fig
- Return type
matplotlib.figure
Examples
To produce a heatmap overview of the first 20 replicas, run
>>> analyser = Analyse(path_to_models, 'quad') >>> fig = analyser.plot_heatmap_overview('ctgre_ctgre', 'quad', 'tt', cut=0.5, reps=np.arange(20)) >>> fig
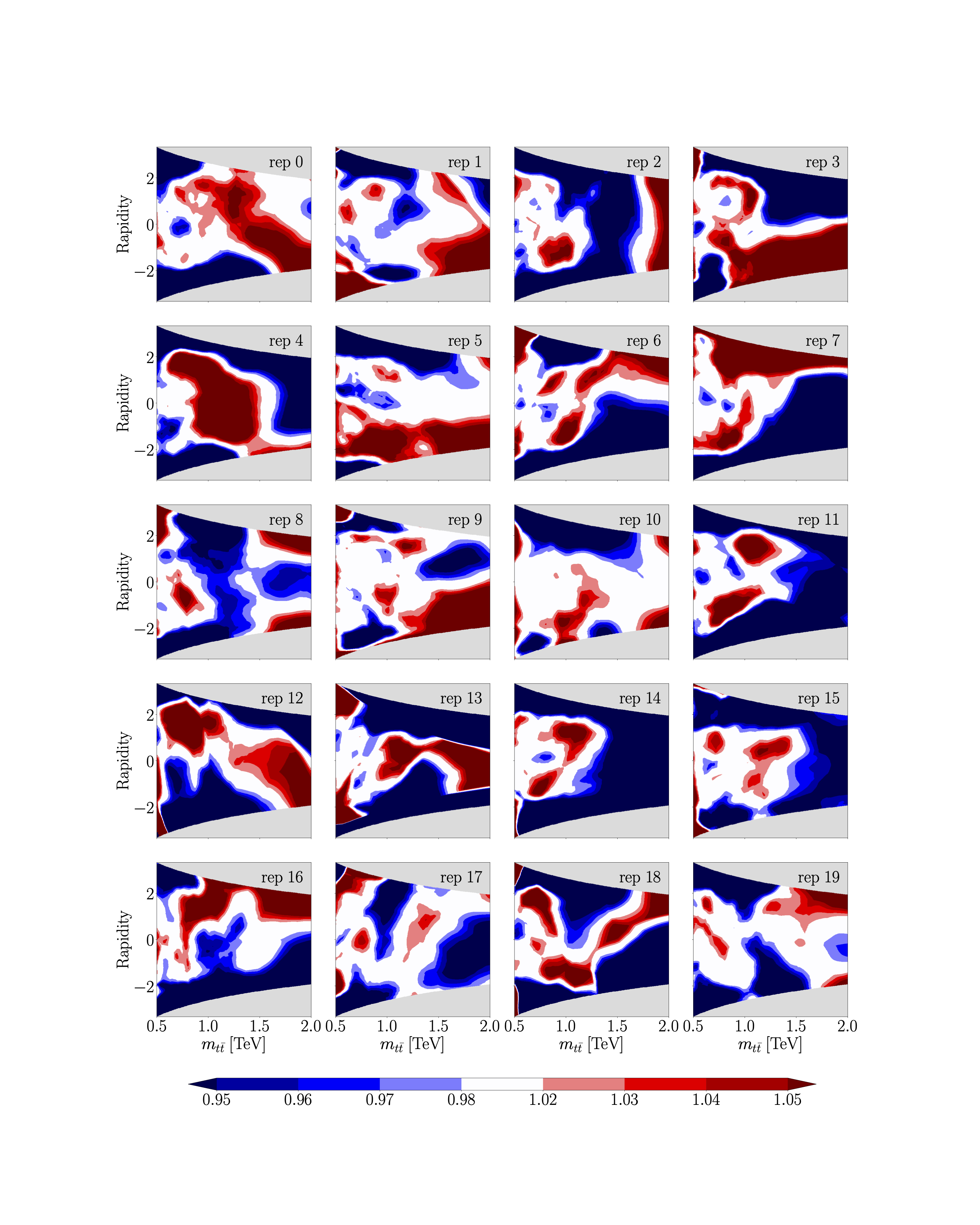
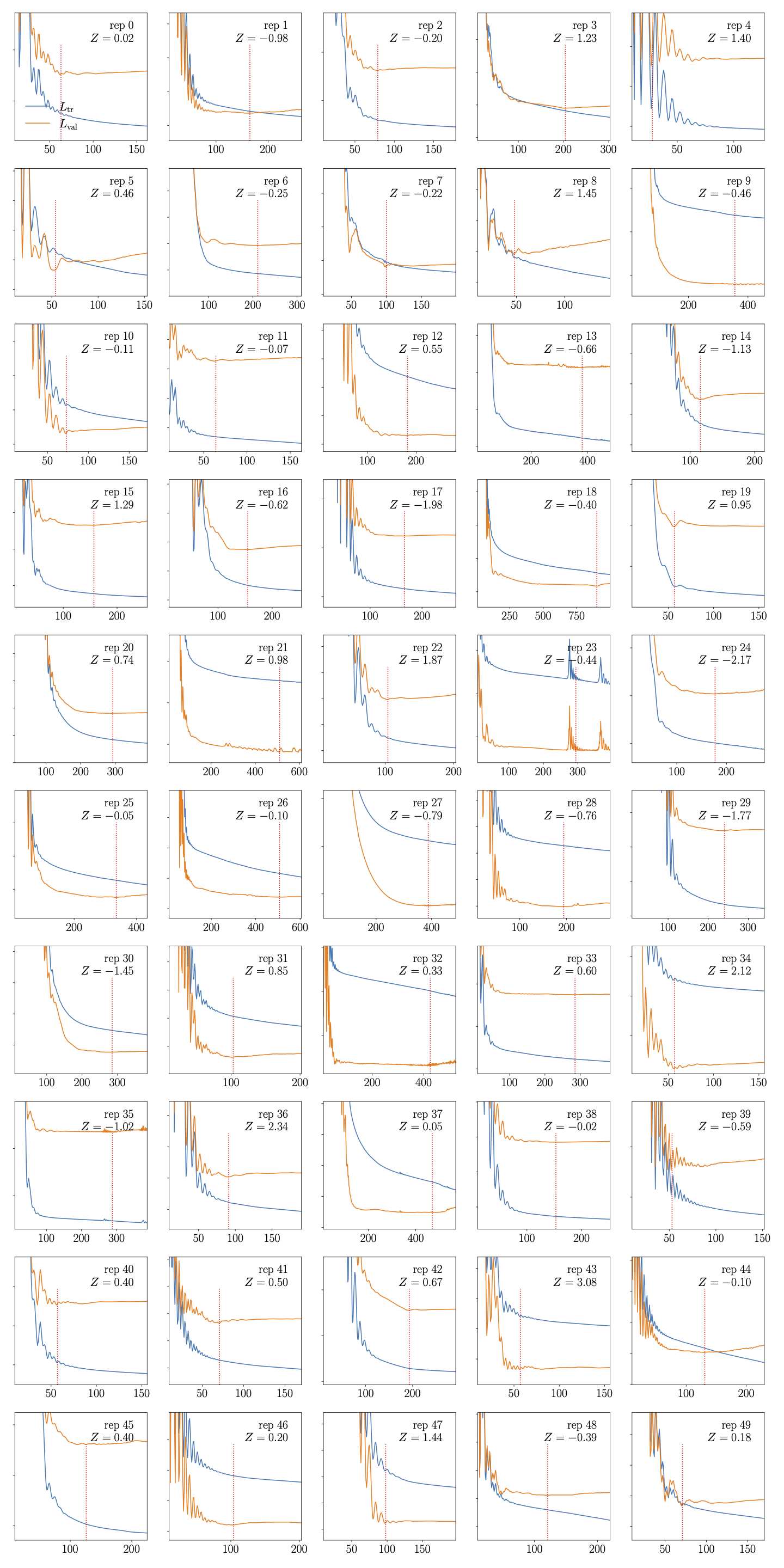
- plot_loss_overview(c_name, order, ax=None, rep=None, xlim=None)[source]#
Plots the loss evolution per replica and returns an overview plot
- Parameters
- Returns
fig (matplotlib.figure) – Loss overview plot
train_loss_best (array_like) – List of ‘best’ training losses
Examples
To plot a loss overview corresponding to the training of \(r_{\sigma}^{(c_{tG}, c_{tG})}\), run
>>> analyser = Analyse(path_to_models, 'quad') >>> fig, train_losses = analyser.plot_loss_overview('ctgre_ctgre', 'quad') >>> fig
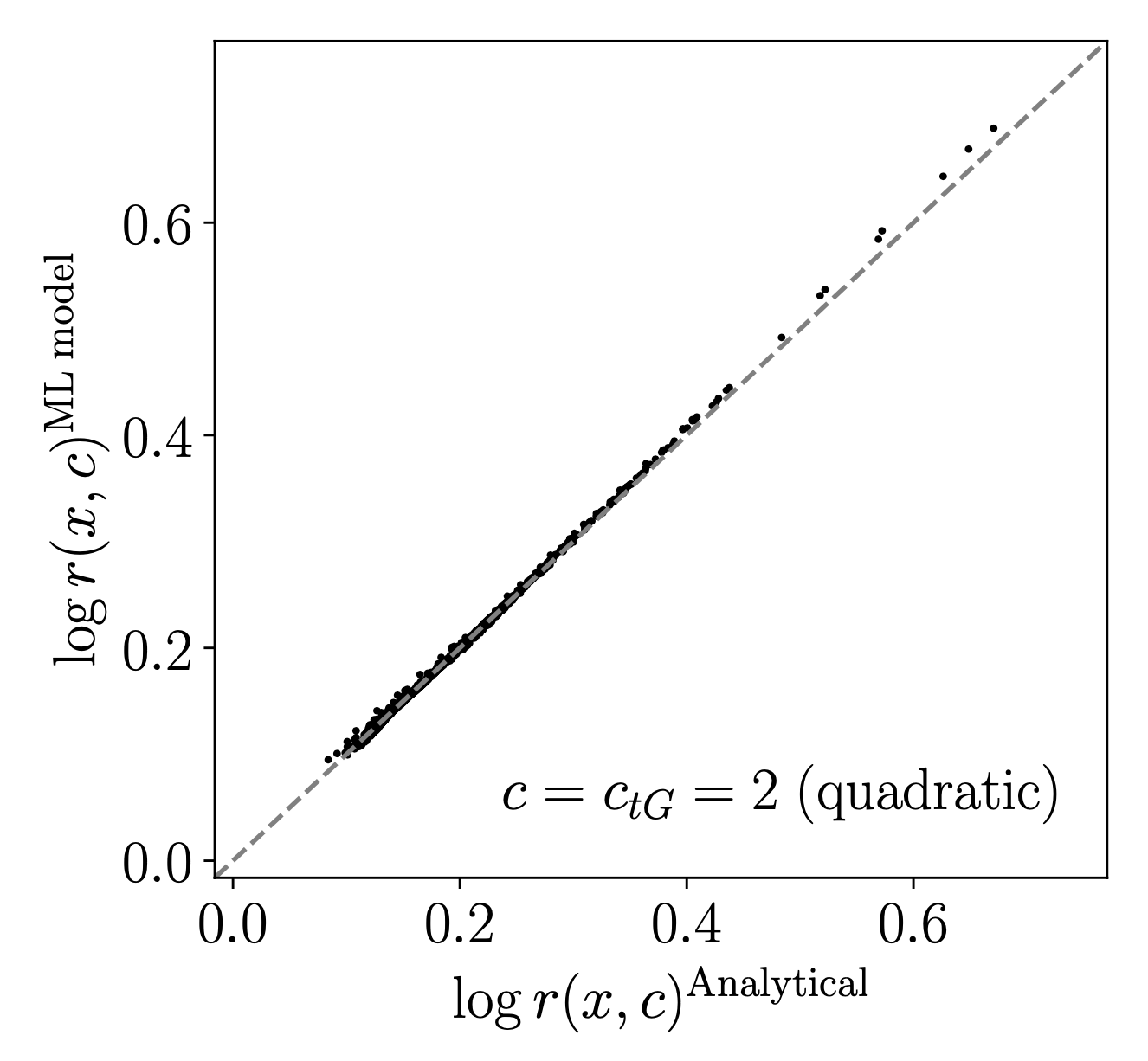
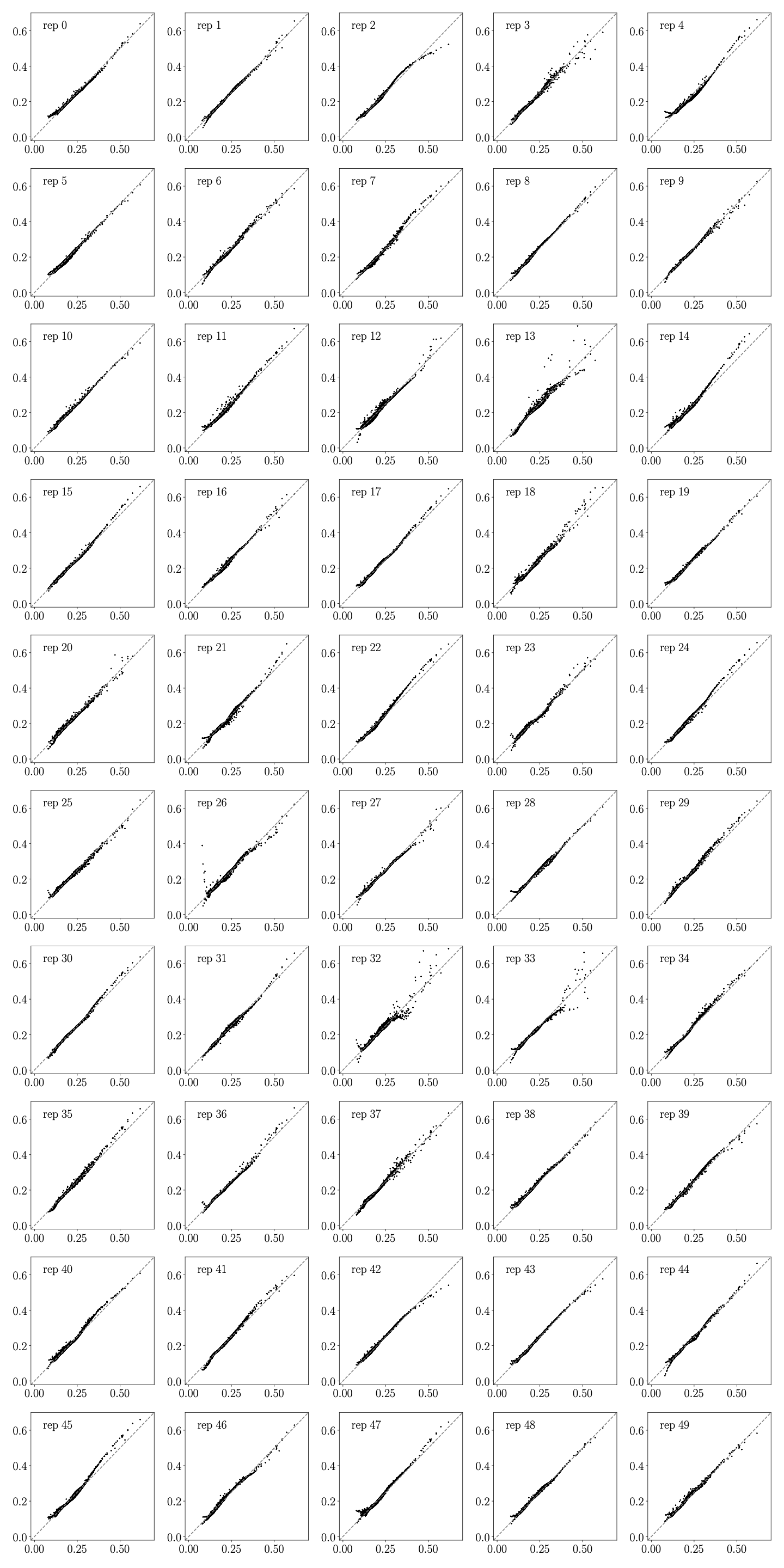
- point_by_point_comp(df, c_name, c, features, process, order)[source]#
Produces a point by point comparison overview per replica of the log-likelihood ratio between the ML model and the analytical (exact) model
- Parameters
df (pandas.DataFrame) – DataFrame with events
c_name (str) – name of EFT ratio function to compare, e.g.
c1_c2c (dict) – Of the form {‘c1’: value, ‘c2’: value}
features (array_like) – List of features to include in the comparison
process (str) – Choose between
ttorZHorder (str) – Specifies the order in the EFT expansion. Must be one of
lin,quad.
Examples
>>> analyser = Analyse(path_to_models, 'quad') >>> fig, ax = plt.subplots()
>>> events_sm = pd.read_pickle('<events_sm_0.pkl.gz>') >>> analyser.point_by_point_comp(events_sm, {'ctgre': -2, 'cut': 0}, ['y', 'm_tt'], 'tt', 'lin') >>> fig

- point_by_point_comp_med(df, c, features, process, order, ax, text=None)[source]#
Produces a point by point comparison of the log-likelihood ratio between the (median) ML model and the analytical (exact) model
- Parameters
df (pandas.DataFrame) – DataFrame with events
c (dict) – Of the form {‘c1’: value, ‘c2’: value}
features (array_like) – List of features to include in the comparison
process (str) – Choose between
ttorZHorder (str) – Specifies the order in the EFT expansion. Must be one of
lin,quad.ax (matplotlib.axes) – Axes object to plot on
text (str) – Additonal text to put on the plot
Examples
>>> analyser = Analyse(path_to_models, 'quad') >>> fig, ax = plt.subplots()
>>> events_sm = pd.read_pickle('<events_sm_0.pkl.gz>') >>> analyser.point_by_point_comp_med(events_sm, {'ctgre': 2, 'cut': 0}, ['y', 'm_tt'], 'tt', 'lin') >>> fig