Kinematic features used as inputs to the neural network
Kinematic features used as inputs to the neural network#
We display here the kinematic features used as inputs to the neural network, calculated both in the SM and at representative points in the SMEFT parameter space.
First, we display the results including only linear contributions from the SMEFT Wilson coefficients:
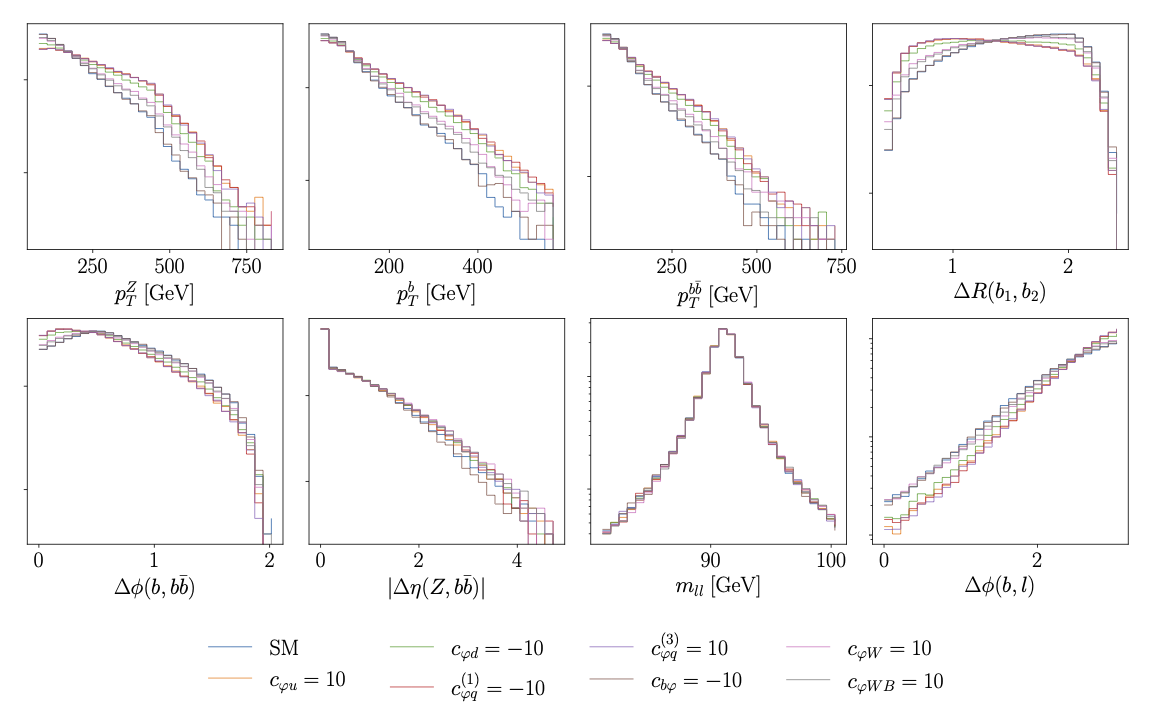
Secondly, we include both linear and quadratic contributions:
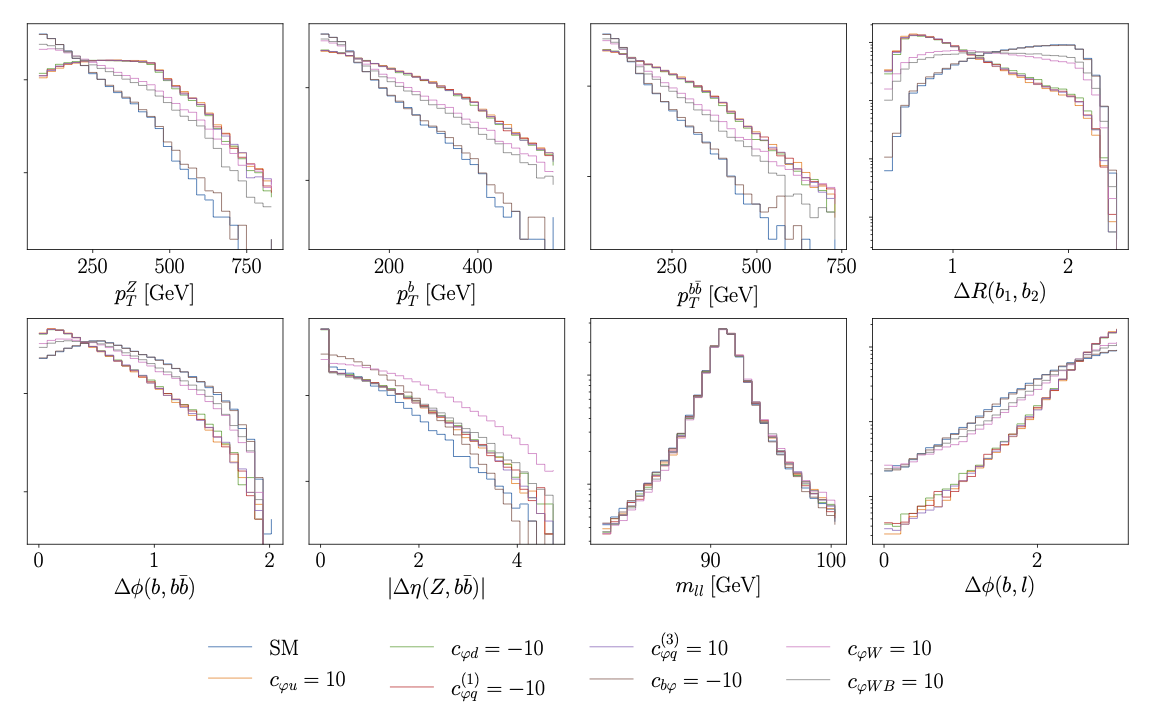
The kinematic features are defined as follows:
Label |
Definition |
|---|---|
\(p_T^{Z}\) |
\(=p_T^{\ell \bar{\ell}}\), the \(p_{T}\) of the dilepton system |
\(p_T^{b}\) |
\(p_{T}\) of the b quark |
\(p_T^{b \bar{b}}\) |
\(p_{T}\) of the \(b \bar{b}\) system |
\(\Delta R(b_{1}, b_{2})\) |
Angular separation between the two b quarks |
\(\Delta \phi(b, b \bar{b})\) |
Azimuthal angle between the \(b\) quark and the \(b \bar{b}\) system |
\(|\Delta \eta(Z, b \bar{b})|\) |
Absolute value of the pseudorapidity difference between the Z and the \(b \bar{b}\) system |
\(m_{\ell \ell}\) |
Invariant mass of the dilepton system |
\(\Delta \phi(b,\ell)\) |
Azimuthal angle between the leading b quark and charged lepton |